Rajasthan, the largest state in India, was historically a region fragmented into 18 princely states, 3 chieftainships and was united only by a term which was coined by the British, ‘Rajputana Agency/Province’, until 1949 AD. Even today a fleeting glance might fool you into thinking that this place is all about deserts and camels to the west, forests and wildlife to the east (and south) and a place where everyone’s mother tongue is Hindi (it is also the official language of the state); but one needs to take a closer look in order to understand that this land is just as geographically, culturally, linguistically and cuisine-wise diverse as any other part of India.
Some of the major historical regions of Rajasthan are Dhundhar (includes Jaipur), Hadoti (includes Kota), Marwar (includes Jodhpur), Mewar (includes Udaipur, Chittorgarh), Shekhawati (includes Churu, Sikar, Jhunjhunu), Godwar (includes Falna, Abu), Mewat (includes part of Alwar, Bharatpur, Dholpur), Vagad (includes part of Banswara and Dungarpur) and Ajmer. While these regions are relatively smaller when compared to the huge size of India; they have their own dialects, their own style of cooking, their own deities, and last but not the least their way of living is in harmony with the geographical conditions (we need to remember that Rajasthan is all desert in the west, semi arid in the north and central, extremely hilly in the south and all green in the east) of their environs.
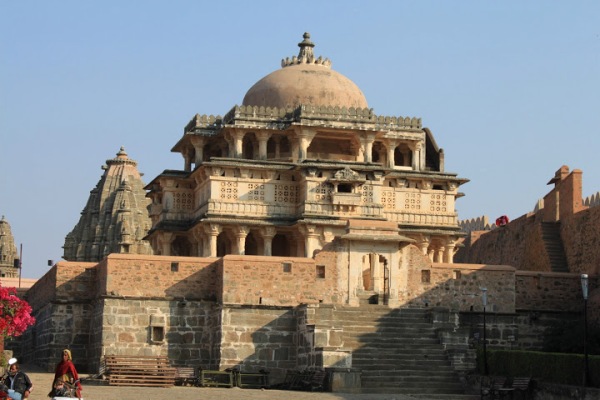
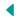
Being such a fragmented region since time immemorial meant that there would be rivalries amongst kingdoms and when differences weren’t resolved through dialogue, war was inevitable. So, from a security point of view it was imperative for all the rulers of Rajasthan to defend their realms and that would mean constructing forts. The more the better, the bigger the better! It is a representation of this fact, that Rajasthan has numerous forts with each built differently as per the local landscape and environs, which prompted UNESCO to choose six of the most unique ones as World Heritage Sites. This article focusses on one such fort, of the Kingdom of Mewar, which is not only one of the oldest in Rajasthan but also one of the most massive ones to be constructed in the history of India, ever!
Located in the wilderness, at a distance of 100 kms from the tourist’s paradise of Udaipur, a fort of gigantic proportion stands; a UNESCO World Heritage Site which a majority of tourists and people, generally, tend to ignore. They don’t ignore this fort because it is not worth looking at, they don’t ignore this fort because it does not have its own legendary stories to tell, they don’t visit this fort simply because they are not aware about this place. The sole aim of writing this article is to correct that anomaly so that whenever a tourist or traveler visits Udaipur or any destination in Rajasthan he/she does not miss out on a monument which has the second largest wall of Asia at 36kms, second only to the Great Wall of China, and some of the finest palaces and temples ever constructed in this region.
Constructed on the orders of Rana Kumbha of Mewar (and hence named after him, Kumbhalgarh simply means the Fort of Kumbha) between 1444 – 1458 AD, this expansive fort was constructed on a series of hills at the border of the realms of Mewar and Marwar. A fort built by a Jain ruler Samprati in the 2nd century BC and some temples located in the same area pre-dated the fort. As per legend when Rana Kumbha’s men could not erect a major bastion he was suggested by an ascetic to conduct a human sacrifice to appease the elements. It is believed that after some futile searching the ascetic offered himself for the sacrifice. The spot of his beheading has a temple there. After this, construction of the fort was undertaken successfully in full swing and as per folklore Rana Kumbha (who ironically was assassinated by his son in the same fort!) burned large lamps to facilitate the construction of fort even during night hours.
Rana Kumbha had a prowess of architecture as well and he had designed (or co-designed) at least 32 of the 84 forts constructed during his lifetime. One of the salient features of this particular fort designed by him and his architect Mandan were the bottle-shaped bastions (bulbous at the base, narrow at the top) whose purpose was to desist escalade warfare (the opposing armies could not prop up their wooden ladders, to storm the fort walls, without the fear of breaking them as they would have been forced to be kept at an angle). These unique bastions were complemented with walls which were over 7 metres wide in some places (enough for 7 horses to run side by side).
This gargantuan fort, replete with palaces (built in Rajput architectural style along with some influences Mughal architecture coming in at later stages), temples (constructed in the Nagara (North Indian) and Maru Gurjara (West Indian) styles of architecture), step wells, dams and multiple levels of defensive walls was a defender’s delight. Historical facts ascertain this fact, that while this fort faced numerous sieges the opposing armies, no matter how qualified and huge they were, could never break into Kumbhalgarh (the only time the Mewar army defending Kumbhalgarh surrendered, in 1578 AD, was when they ran out of ammunition!). It is no wonder that whenever rulers of Mewar felt threatened they would head here for safety.
This fort’s importance can be judged from the fact that it was here that the toddler Rana Uday Singh was sneaked here (in 1538 AD) to prevent him from being assassinated following a palace coup, by Panna Dhai. The legendary Maharana Pratap, the eldest son of Rana Uday Singh, was born here (on May 9th 1540 AD), in the ‘Jhalia ki Malia’ (Palace of Queen Jhalia). Some decades hence when Maharana Pratap lost the, furiously fought, Battle of Haldighati (1538 AD) it was to Kumbhalgarh where he headed to and even though Mughal emperor Akbar laid an elaborate siege to capture him he managed to leave the fort successfully, after he ran out of ammunition.
This fort was restored, at some places, and renovated by Maharana Uday Singh II in 1905 AD. He restored the battlements, the bastions and built the wonderful Badal Mahal after pulling down some old structures.
Some of the major monuments which stand out from the rest in Kumbhalgarh are the Char Bhuja Temple (near Ram Pol), Baavan Deori Temple (a unique Jain Temple with 50 minor and 2 major sanctum sanctorums!), Badal Mahal, Rana Kumbha’s Palace, Ganesh Temple, Neelkanth Mahadev Temple amongst others.
Once the rulers of Mewar relinquished their claim over Kumbhalgarh, which happened the moment they signed the Instrument of Accession in 1949 AD, the royal sheen went away from this place. What’s left now is a couple of villages, inside the fort premises, whose inhabitants claim to be descendants of the royal servicemen appointed as caretakers of the fort.
Even today, if one takes a walk over the impenetrable walls of this over 500 years old fort, the eerie silence present there would serve as a catalyst and enable one to feel the vibes of the bloody battles which were fought here by the defenders against a rampaging army to keep the fort and their sovereign safe, even at the cost of their lives.
The Hill Fort of Kumbhalgarh might have been neglected by a majority of tourists and history enthusiasts of the world since quite some decades now, but it would take them only one visit to realise what Emperor Akbar’s great armies and other foes of the Mewar rulers felt when they gazed upon this fort, it’s ‘brute strength’.